Industrial ventilation systems for potentially explosive atmosphere
Components and design for ATEX applications
We already dealt with ATEX themes, from a formal point of view, focusing on the latest 2014/34/EU directive and the previous one (94/9/EC). As we saw, this directive aims to guarantee the free circulation of products used in potentially explosive atmospheres within the European Community.
But in practice, from a concrete perspective, how should plants be designed for a use in potentially explosive atmospheres?
What features must components have? How to act in the event of an explosion?
The purpose of this article is to answer these questions and some others!
ATEX zone classification
Before answering previous questions, it is better to clarify two aspects related to ATEX directive:
- elements necessary for the occurrence of a potentially explosive atmosphere
- classification of ATEX zones
The first aspect is referred to combustion: combustion occurs when fuel, comburent and spark are present simultaneously.
Without one of these three elements we cannot speak of a potentially explosive atmosphere and, consequently, we do not fall under the scope of application of ATEX directive.
The second aspect, as we already explained in the article “General content of 94/9/EC European Directive“, is a matter of classification. In fact work areas are classified into zones according to frequency and duration of explosion risk in atmosphere due to gas presence (in this case we talk about atex zones 0, 1 or 2) or to dust (so talking about atex zones 20, 21 or 22).
Let’s focus on explosive dusts now: talking about dust, we will take into consideration following classified areas:
- Zone 20 = an atmosphere where a cloud of combustible dust is present frequently, continuously or for long periods;
- Zone 21 = area in which the formation of an explosive atmosphere is occasional;
- Zone 22 = area in which the formation of an explosive atmosphere is not probable and, if it occurs, it would be of short duration;
Systems positioned in zone 20 or 21, due to greater risk of explosion, must be certified by special Bodies and must be equipped with double safety systems with consequent increase in construction costs.
For this reason, it is recommended to place the abatement system outside the production area (usually zone 22). In the latter case the plant must be equipped with a single safety system and self-certification is sufficient to certify its compliance with the ATEX directive.
KST and Pmax: dust explosive energy parameters
When designing an ATEX system, dust’s characteristics are a fundamental driver for technical choices. On this regard, two important parameters to acknowledge perfectly are:
- Kst = It is a dust deflagration index, an explosion constant that measures the speed of pressure increase during a dust explosion. It is measured in bar m/sec. and also gives an indication of the spread of the flames.Kst represents a fundamental parameter for sizing the safety panel (see details below);
- Pmax = It is an index representing maximum pressure developed by an explosion coming from dust. It is measured in bars
Kst and Pmax indicate how destructive an explosive dust can be when this event occurs.
ATEX security systems and design focal points

Filters intended for use in ATEX atmosphere must be designed to withstand the explosion pressure which varies according to the characteristics of the dust and of the production system. For this reason, ATEX filters both bag filters and cartridges once, as well as activated carbon filters, are equipped with a number of security systems.
Safety panels
In event of explosion anti explosion panels break up and release the deflagration towards the outside avoiding the explosion of the filter. This system works if filters are designed to withstand higher pressures than the safety panels.
Dust discharge system
Particular attention must also be paid to the choice of the dust discharge system which must be realized in ATEX version. One of the most used solution is the rotary valve: component that allows the continuous discharge of dust coming from the hopper or from the cochlea avoiding accumulation of the pollutant inside the filter.
In its ATEX version a rotary valve shall be designed in order to avoid creation of sparks.
No-return valve
The non-return valve is a device used to avoid propagation of the explosion in the suction line and, consequently, in the production area. It is usually placed between the filter and the work environment and, in event of a deflagration, this valve acts as a physical block, diverting the air flow towards the outside part of the system, allowing the explosion to break through the safety panel (or other systems).

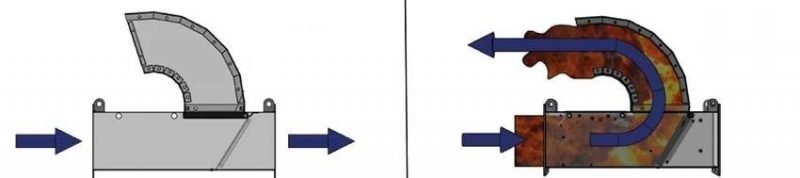
Explosion diverters
Like non-return valves, the explosion diverter is placed between filter and work environment to avoid the propagation of the explosion in the production area. As you can see from the image below, in event of an explosion the flow path is diverted towards a safe, or safer areas.
Partition shutters
The compartmentation shutters can be of different types (sash, butterfly etc.) and are used to segregate sections of the filter containing gaseous flow coming from different production departments.
They are placed in the central suction pipe and, in case of explosion or fire, they intervene instantaneously isolating the interested area.
Explosion suppression system
Explosion suppression system can be compared to a fire protection system because it is able to detect explosions in their initial phase and quickly suppress them. In event of a deflagration, a special detector sends a signal to the control unit that commands the opening of cylinders containing a chemical agent able to suffocate the explosion in a few milliseconds, so avoiding the huge pressure increment inside the filter consequent to an explosion event.
This component is used as a second security system in zones 20 and 21
Flame arrestors
Flame arrester system is generally used when the abatement system is placed inside a warehouse. It allows to circumscribe flames, preventing them from spreading outside so affecting the work environment.
Up to know we have analyzed safety systems, but the plants are also made up of other components (fan, pressure switch, pipes, etc.). When aspiration and filtration systems are intended for use in a potentially explosive atmosphere, all the components must be designed according to the ATEX classification of the different areas.
What happens after an explosion?
To end this article, let’s answer the last question: How to act in the event of an explosion?
Let’s start by saying that, after an explosion, specialized technicians must intervene to check the general condition of the filter and ensure compliance with 2014/34/EU directive (ATEX).
Among the safety components, those that are most affected by the explosion are the safety panels which, as we have seen, break up to release the deflagration towards the outside. After the explosion they are replaced, but it is also necessary to verify all internal filtering elements (sleeves or cartridges) and other elements that could be damaged by the event. After the technical inspection, the system must certified again, to ensure that it complies with the ATEX directive.

Contact Tecnosida to receive more information and follow our newsletter for new updates!